The Expansion Of Small Motor Use In Home Appliances
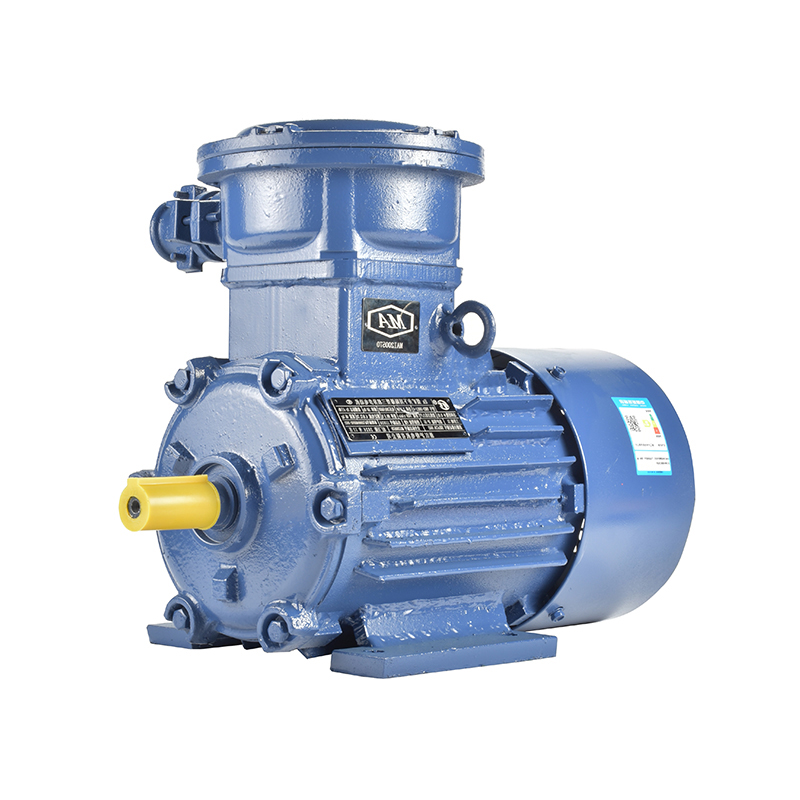
One noteworthy aspect is the gradual incorporation of motor types such as the industrial induction motor into domestic appliances. While industrial induction motors are traditionally associated with heavy-duty machinery and manufacturing equipment, their design principles offer valuable benefits when scaled appropriately for home use. These motors are known for their durability and reliability, traits that appeal to appliance manufacturers aiming for long-lasting products. For example, induction motors in washing machines and refrigerators provide stable operation and reduced maintenance, helping these appliances maintain consistent performance over extended periods.
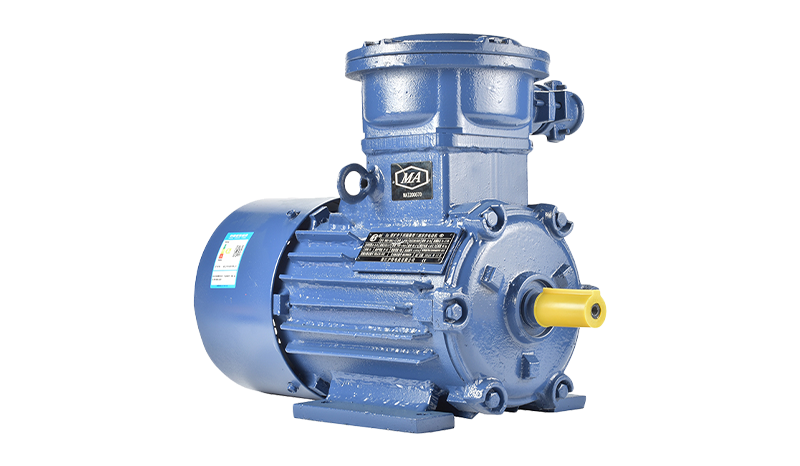

Beyond industrial induction motors, the home appliance sector is increasingly experimenting with high torque permanent magnet motors. These motors stand out for their ability to generate significant torque while maintaining a compact size, making them well-suited for appliances where space and power efficiency are both critical. High torque permanent magnet motors have found applications in devices such as vacuum cleaners and power tools used around the home. Their precise control and rapid response capabilities contribute to smoother operation and better energy utilization, which is a growing concern among consumers conscious of electricity consumption.
In addition to rotary motors, the adoption of more specialized motors like the permanent magnet linear synchronous motor (PMLSM) is gradually expanding in the home appliance market. PMLSMs differ from traditional rotary motors by producing linear motion directly, which eliminates the need for complex mechanical conversion systems. This characteristic can advance to quieter and more compact designs, especially beneficial in appliances such as robotic vacuum cleaners or automated window shades. The precise movement and high efficiency of permanent magnet linear synchronous motors are increasingly valued in smart home devices that require smooth and silent operation.
The expansion of small motor use in home appliances is also linked to the growing demand for smart and energy-efficient products. As appliances become more interconnected through the Internet of Things (IoT), motors need to support more nuanced control schemes and variable speeds. Advanced motor technologies like the high torque permanent magnet motor provide greater flexibility in controlling appliance functions, enabling features like variable suction power in vacuum cleaners or adjustable spin speeds in washing machines. These capabilities contribute to better user experiences and can help extend the lifespan of appliances by adapting motor performance to actual usage conditions.
Another driver behind this trend is the push for environmental sustainability. More efficient motors help reduce the overall energy consumption of household appliances, which can lower utility costs and reduce environmental impact. While industrial induction motors have long been recognized for their efficiency in industrial settings, their principles are now being adapted to smaller sizes without sacrificing performance. Similarly, the efficiency gains from permanent magnet motors, including the linear synchronous variants, align well with stricter energy standards adopted by many regions worldwide.
The integration of these motor types into home appliances also influences design trends. Manufacturers are finding new ways to embed motors seamlessly into appliance structures without compromising on aesthetics or compactness. High torque permanent magnet motors, due to their size and torque capabilities, enable thinner and lighter designs. Permanent magnet linear synchronous motors, with their ability to produce direct linear motion, reduce the need for bulky gears or belts, thus contributing to sleeker and quieter devices.
Despite these advances, challenges remain in expanding small motor use in home appliances. Cost considerations continue to influence which motor types are feasible for different product segments. Industrial induction motors, for instance, might require modifications to fit cost-sensitive markets without losing their reliability advantages. Similarly, the precision manufacturing needed for permanent magnet linear synchronous motors can increase production complexity. However, as manufacturing technologies improve and economies of scale are achieved, these hurdles are gradually being addressed.
Overall, the expansion of small motor use in home appliances reflects a broader trend of technological transfer from industrial applications to consumer markets. Motors that once powered large machinery are now being engineered to enhance everyday household devices in ways that improve efficiency, functionality, and user comfort. Whether through industrial induction motors providing steady performance, high torque permanent magnet motors enabling compact power, or permanent magnet linear synchronous motors offering smooth linear motion, the variety of motor technologies enriches the home appliance landscape.
As consumer expectations evolve and environmental standards become more stringent, it is likely that the range and sophistication of small motors in home appliances will continue to grow. Manufacturers who can balance performance, cost, and design considerations will be well-positioned to meet these emerging needs. The journey of these motor technologies from factory floors to kitchen counters and living rooms is an ongoing story of innovation and adaptation, shaping how we interact with the appliances that have become essential in modern life.
-
Feedback


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى






