Sustainable Materials In Motor Production: What’s Changing
In recent years, the motor manufacturing industry has witnessed a gradual but clear shift towards sustainable materials and eco-friendly production methods. This transformation is driven by increasing environmental awareness, stricter regulations, and customer demand for greener products. From single phase and 3 phase motors used in everyday applications to specialized products such as BLDC synchronous motors and explosion proof brake motors, manufacturers are reconsidering the materials and processes used in motor production.

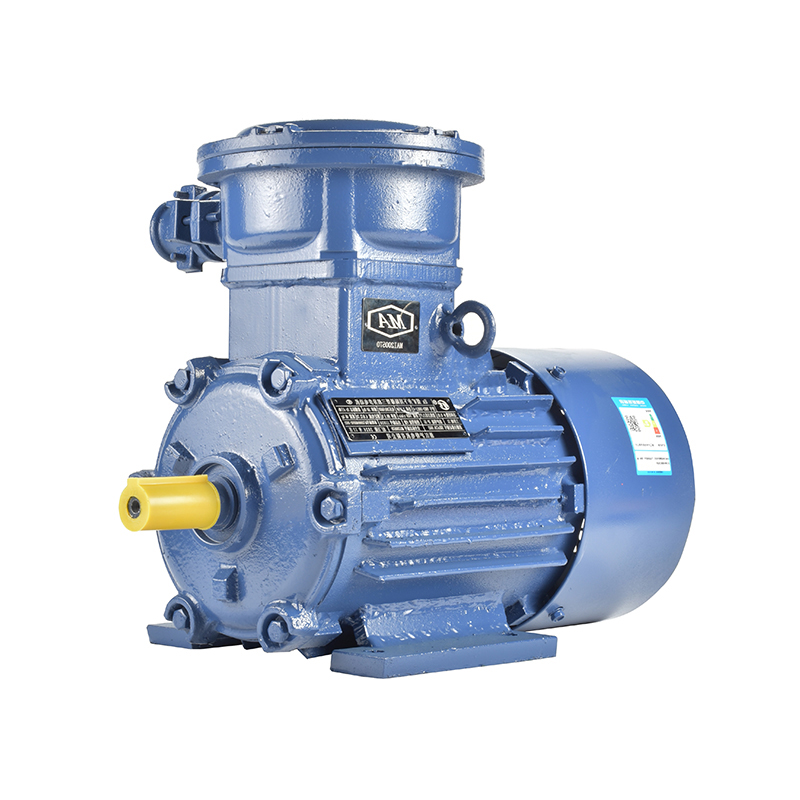
Traditionally, electric motors have relied on materials like copper for windings, steel for the core and housing, and various insulating plastics. While these materials have proven effective for performance and durability, they come with environmental drawbacks. Copper mining and refining, for instance, consume significant energy and generate waste, while some plastics used in insulation and components are derived from non-renewable petrochemicals and are difficult to recycle. To address these concerns, the industry is exploring sustainable alternatives without compromising on motor quality and reliability.
One area of change involves the use of recycled and recyclable metals. Steel and aluminum alloys are increasingly sourced from recycled material streams. These metals are essential in the motor housing and rotor components. Using recycled steel reduces energy consumption by a significant margin compared to primary steel production. Similarly, aluminum alloys made from recycled sources help reduce the carbon footprint of motor manufacturing. This shift is relevant across various motor types, including single phase and 3 phase motors, which represent a large portion of industrial and commercial electric motors.
For copper windings, some manufacturers are testing the use of copper scrap and recycling initiatives to lessen raw material extraction. However, the challenge lies in maintaining electrical conductivity and mechanical integrity after multiple recycling cycles. To support this, innovations in copper refining and processing are under development, aiming to close the loop in copper use within motor production.
The trend toward sustainable materials also extends to insulation and other non-metallic components. Traditional insulating materials, such as certain phenolic resins or PVC-based plastics, have environmental and health concerns, including toxicity during manufacturing or disposal. In response, new bio-based or recyclable polymers are being introduced. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but also help improve motor recyclability at the end of product life. For example, biodegradable polymer films or thermoplastic resins are being tested as alternatives for stator insulation and terminal boxes.
Specialized motors like the BLDC synchronous motor, known for its energy efficiency and compact size, are also benefiting from sustainable material innovation. The magnets used in BLDC motors often contain rare earth elements, the extraction of which raises environmental and ethical issues. Research is ongoing to reduce rare earth content, develop alternative magnet materials, or improve magnet recycling methods. Sustainable sourcing and circular economy practices are becoming part of the strategy to produce more environmentally friendly BLDC synchronous motors.
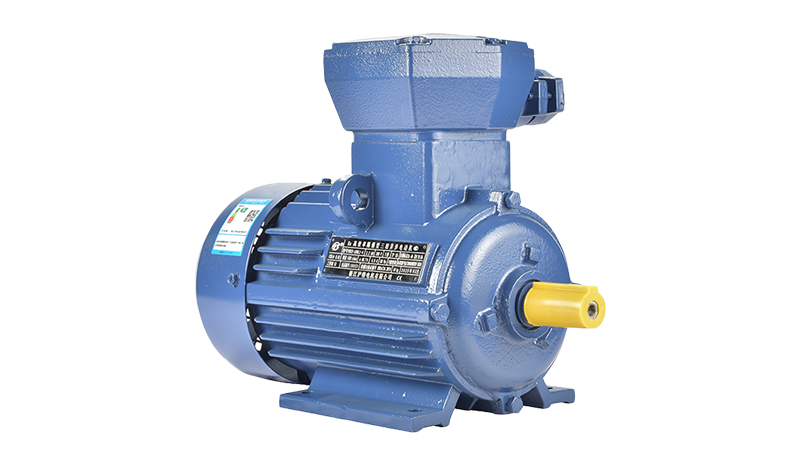
Explosion proof brake motors represent another category where sustainable materials are gaining traction. These motors are used in hazardous environments, such as chemical plants or mining operations, where durability and safety are paramount. The protective housings and braking components require materials that withstand harsh conditions while aligning with sustainability goals. Advances in composite materials and coatings that extend product life and reduce maintenance contribute to more sustainable solutions for explosion proof brake motors. Moreover, using corrosion-resistant, recyclable metals helps reduce environmental impact during manufacturing and disposal phases.
In addition to materials, motor producers are examining their entire production process to align with sustainability. This includes reducing waste, less energy consumption, and adopting cleaner technologies. For instance, processes like powder coating and advanced finishing methods reduce harmful emissions compared to traditional painting. Lean manufacturing principles help reduce material waste, and water-based lubricants and coolants replace petroleum-based alternatives in machining.
The adoption of sustainable materials and practices does come with challenges. Manufacturers must balance cost, performance, and environmental benefits while ensuring compliance with industry standards and customer expectations. Material substitutions may require extensive testing to maintain motor reliability and safety. However, the gradual integration of sustainable materials is creating opportunities for innovation and differentiation within the motor industry.
Ultimately, the move towards sustainable materials in motor production reflects a broader commitment to environmental responsibility. Whether in widely used single phase and 3 phase motors, energy-efficient BLDC synchronous motors, or robust explosion proof brake motors, the changes in materials contribute to reducing the ecological footprint of electric motor manufacturing. As technology advances and sustainable options become more viable, the industry is expected to continue this positive trajectory toward greener production methods.
-
Feedback


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى






