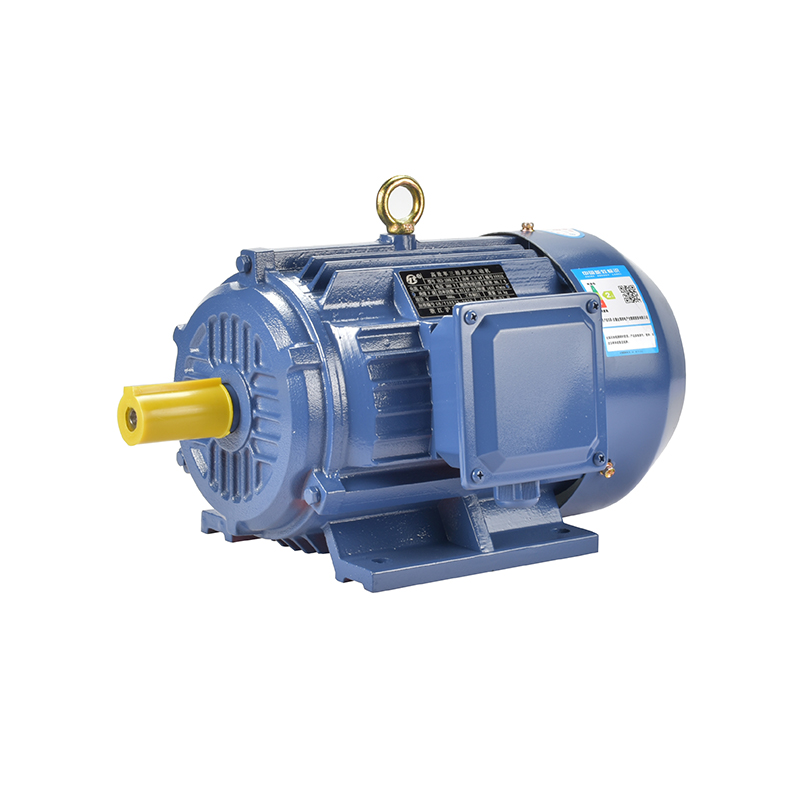
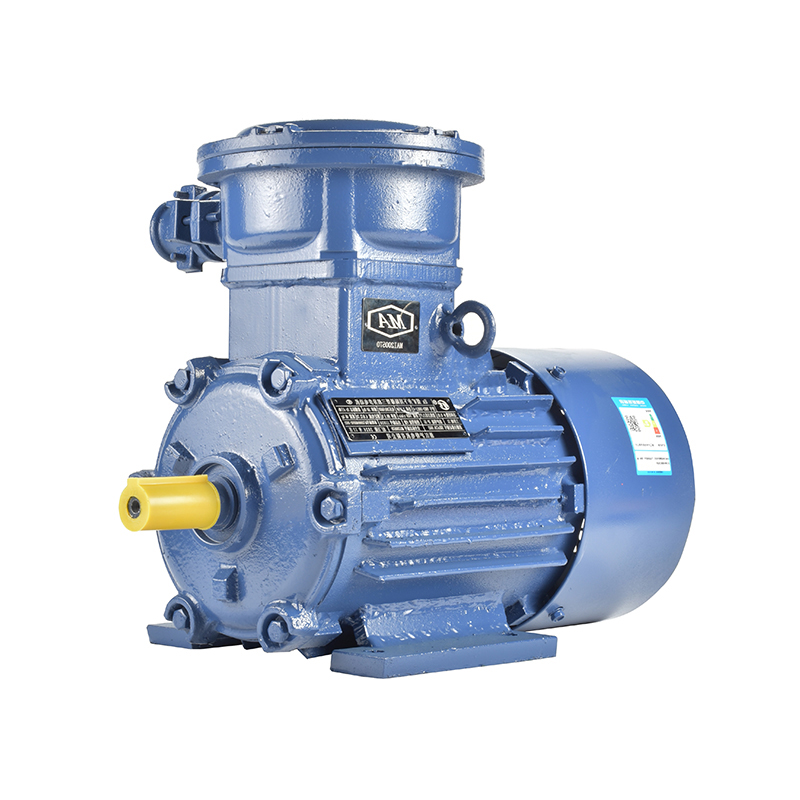
Global Market Trends: Why Second Class Energy Efficient Motor Is Becoming a Policy Priority
In recent years, energy efficiency has become a top priority for many countries aiming to balance industrial growth with environmental protection. Across manufacturing, construction, and public infrastructure, a new generation of equipment is emerging to meet this challenge — and among them, the Second Class Energy Efficient Motor stands out as a key player. This technology is gaining attention not only for its engineering advantages but also for its alignment with global sustainability policies.
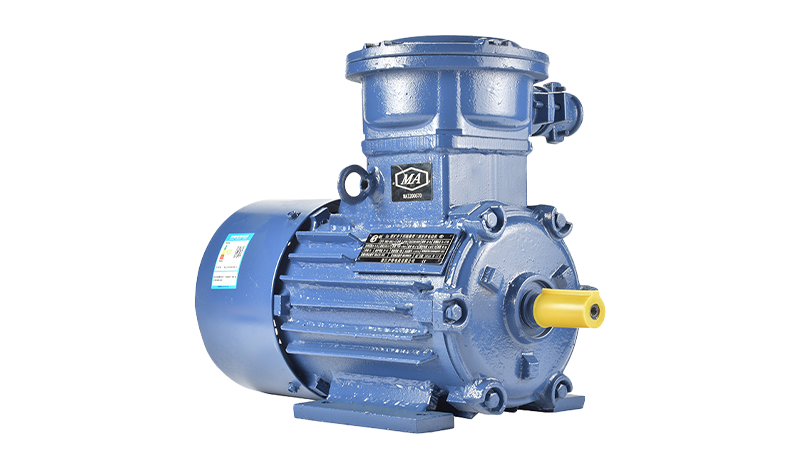

Shifting Global Regulations Toward Energy Efficiency
Around the world, governments are implementing stricter regulations to curb energy waste and carbon emissions. From the European Union’s energy efficiency directives to Asia’s green industrial transformation goals, compliance has become a necessary part of doing business. Motors are one of the largest electricity consumers in industrial environments, so upgrading to a Second Class Energy Efficient Motor helps companies meet regulatory requirements more easily. These motors reduce unnecessary energy loss, helping industries transition toward more sustainable production models.
A Strong Response to Economic and Environmental Pressure
As energy prices continue to fluctuate and the effects of climate change become more visible, both consumers and industries are reassessing how energy is used. The Second Class Energy Efficient Motor fits perfectly into this trend, offering reliable performance while using less power. For companies in heavy manufacturing or continuous production sectors, this means lower operating costs and reduced carbon footprints. In many regions, businesses that adopt energy-efficient equipment can also qualify for tax incentives or green financing programs, making the switch even more worthwhile.
Growing Industrial Demand and Market Expansion
The global motor market is evolving rapidly. Analysts note that the demand for efficient motors is growing not only in developed markets but also in emerging economies where industrial expansion is accelerating. The Second Class Energy Efficient Motor is increasingly adopted in applications such as HVAC systems, water pumps, conveyors, and automation equipment. Its flexibility and adaptability make it a strong choice for both retrofitting existing systems and powering new, eco-friendly production facilities.
In addition, large-scale infrastructure projects—such as smart grids and renewable energy systems—are driving increased use of efficient motors. These projects rely on dependable, energy-saving equipment to deliver consistent performance and comply with environmental standards.
Policy Support Encouraging Industrial Transformation
Government policies are now actively promoting energy-saving technologies through subsidies and certification systems. The Second Class Energy Efficient Motor often qualifies under such programs, giving it a competitive edge. This policy environment encourages industries to phase out low-efficiency motors and adopt higher-performing alternatives. For manufacturers, meeting these energy efficiency classes is no longer optional—it’s a requirement for remaining competitive and maintaining export eligibility in international trade.
A Clear Direction for the Future
The global direction is clear: energy-efficient technologies are shaping the next generation of industrial progress. The Second Class Energy Efficient Motor plays a critical role in this transformation, connecting environmental goals with economic benefits. As industries continue to modernize, these motors will not only enhance productivity but also reinforce a shared commitment to sustainability and responsible energy use.
By adopting the Second Class Energy Efficient Motor, businesses are preparing themselves for a market where efficiency, compliance, and innovation move forward together—defining the new standard of industrial development worldwide.
-
Feedback


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى






