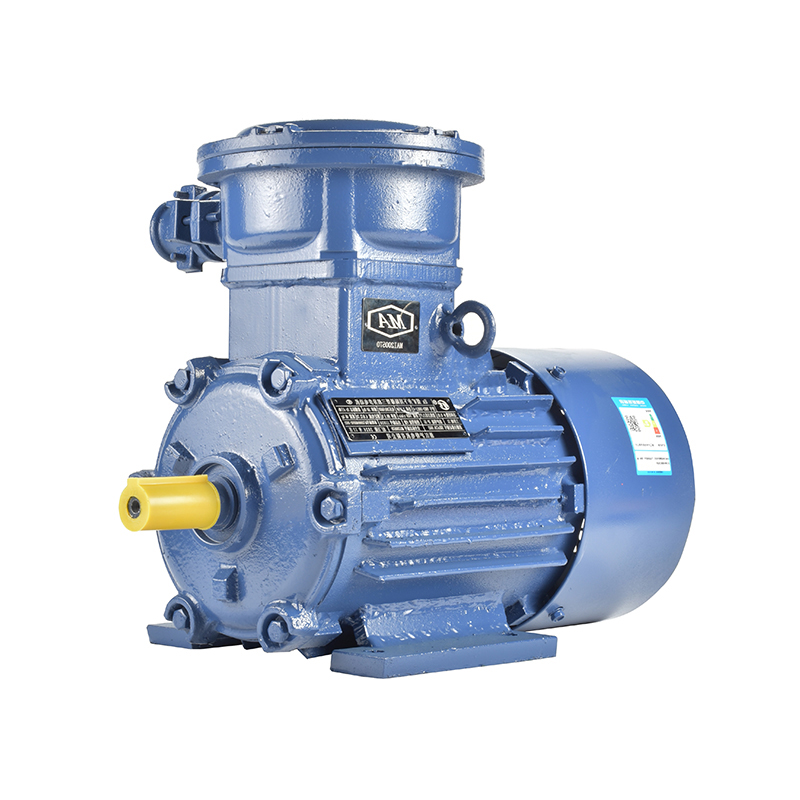
Influence Of Low-Carbon Strategies On Motor Design
As global awareness of climate change grows, industries worldwide are increasingly adopting low-carbon strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The electric motor industry, which plays a crucial role in powering countless machines and systems, is also experiencing a shift driven by sustainability goals. Low-carbon strategies influence how motors are designed, manufactured, and applied, particularly when it comes to common types such as single phase and 3 phase motors, single phase AC motors, and advanced models like PMSM and DC motors.
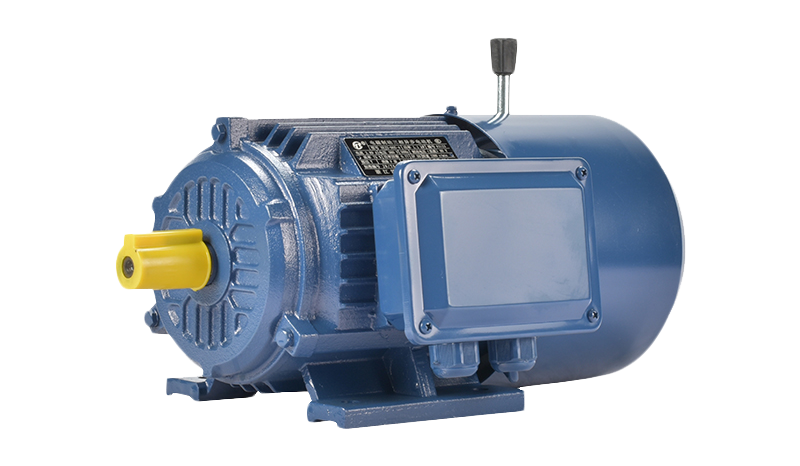

Electric motors consume a significant portion of industrial and commercial energy worldwide, so improving their efficiency is key to lowering carbon footprints. Traditional motor designs are being re-evaluated to reduce energy losses during operation. This rethinking involves changes in materials, motor construction, and control technologies that collectively help meet stricter emissions and efficiency standards.
Single phase motors have been widely used in residential and small commercial applications due to their simple construction and compatibility with common power supplies. Single phase AC motors, for example, power household appliances, small pumps, and fans. While convenient, these motors generally have lower efficiency compared to three-phase motors, partly because of the power delivery method. To align with low-carbon initiatives, manufacturers focus on optimizing the internal components of single phase motors—such as improving winding techniques and reducing friction in bearings—to decrease energy waste.
On the other hand, 3 phase motors are more common in industrial settings because they provide smoother torque and higher efficiency. They are often used in larger machines, conveyor systems, and HVAC equipment. The inherent design of 3 phase motors allows for better power distribution and less vibration, which translates to energy savings during operation. Low-carbon strategies encourage further refinement of these motors through advanced materials like high-grade electrical steel and improved insulation, as well as more precise manufacturing processes to less losses.
In recent years, the integration of permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM) and DC motors has become an important trend in energy-conscious motor design. PMSM motors utilize permanent magnets in the rotor, which helps reduce electrical losses compared to traditional induction motors. This design choice results in higher efficiency, especially under variable load conditions, which is common in applications such as electric vehicles, robotics, and precision equipment. DC motors, with their simple speed control and high starting torque, also benefit from innovations that reduce carbon emissions by optimizing power consumption.
Low-carbon strategies are not only influencing the internal motor design but also extending to the motor control systems. Variable frequency drives (VFDs) and advanced controllers are used increasingly with all motor types—from single phase AC motors to PMSM and DC motors—to fine-tune the speed and torque output. By adjusting motor speed to match actual load demands rather than running at full speed continuously, these control systems significantly reduce unnecessary energy use and related emissions.
Manufacturers also face challenges balancing cost and environmental performance. Incorporating materials such as precious earth magnets for PMSM motors can improve efficiency but comes with price and supply chain concerns. Similarly, optimizing single phase and 3 phase motor designs to reduce energy losses requires precise engineering and advanced production technologies, which may increase upfront costs. However, long-term operational savings and compliance with emerging regulations make these investments worthwhile.
From a broader perspective, the motor industry’s move toward low-carbon design also reflects a shift in customer expectations. End users in sectors like manufacturing, agriculture, and commercial facilities are increasingly seeking motors that not only deliver performance but also contribute to sustainability goals. This demand encourages innovation in product development and encourages partnerships with research institutions to explore new materials, cooling techniques, and motor topologies that align with carbon reduction targets.
Energy efficiency labels and government incentives are also driving the evolution of motor design. Regulations in many countries now set less efficiency levels for single phase and 3 phase motors sold in the market. These policies push manufacturers to adopt low-carbon strategies as a standard practice, ensuring that new motor products consume less energy and produce fewer emissions during their operational lifetime.
In conclusion, low-carbon strategies have a clear influence on the design of various types of electric motors. Whether it is single phase AC motors used in everyday appliances, robust 3 phase motors in industrial settings, or sophisticated PMSM and DC motors applied in emerging technologies, sustainability considerations shape material choices, design methods, and control systems. While challenges remain, ongoing improvements contribute to a gradual reduction in the carbon footprint of motor-powered equipment, supporting a more environmentally responsible future for industrial and commercial operations.
-
Feedback


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى






