Exploring The Impact Of Electrification Policies On Motor Demand
As industries shift toward greener technologies and more energy-efficient solutions, the demand for different types of electric motors has been influenced significantly. This article explores how electrification policies affect motor demand, focusing on three key motor types: the three phase AC servo motor, variable frequency motor, and fixed magnet motor.

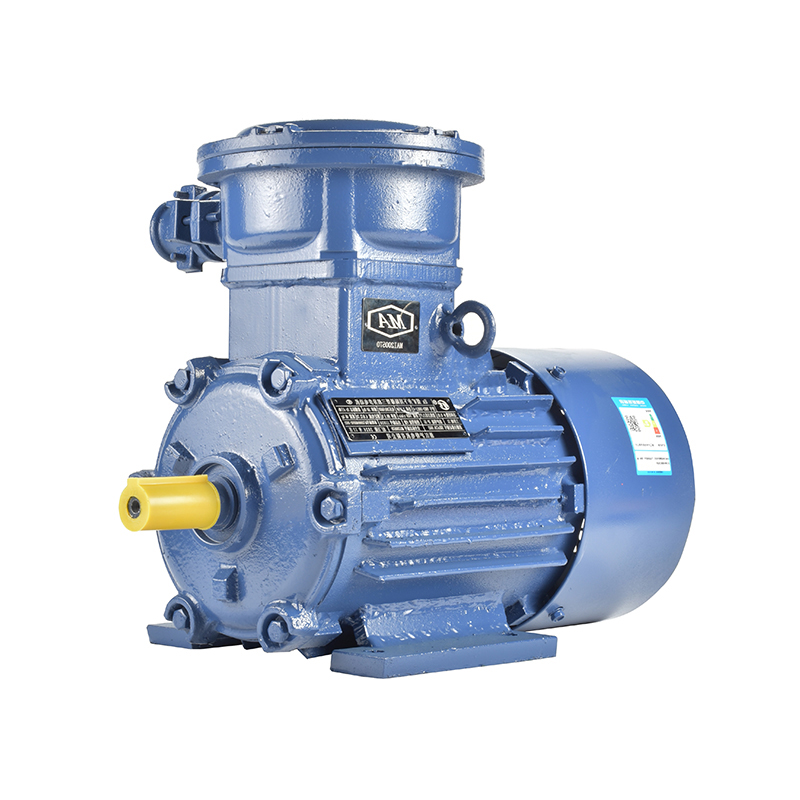
Electrification policies often emphasize energy efficiency and the reduction of fossil fuel dependence. This shift pushes manufacturers and end-users to consider electric motors that offer precise control, improved energy consumption, and adaptability to changing operating conditions. Among these, the three phase AC servo motor has gained attention for its role in automation and precise motion control. The servo motor’s ability to provide accurate positioning and speed regulation makes it a vital component in industries moving toward automated, electric-driven machinery. Policies encouraging industrial automation to improve energy efficiency have contributed to increased interest in servo motor applications, especially in manufacturing sectors.
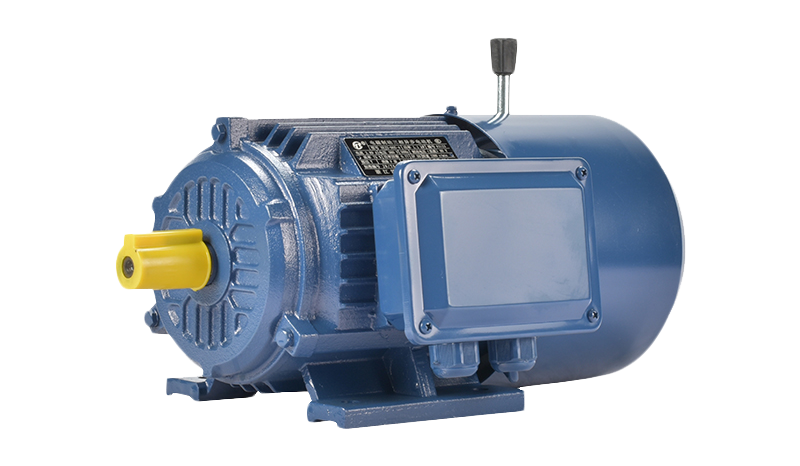
Variable frequency motors also play a significant role in the context of electrification. These motors work with variable frequency drives (VFDs) that allow precise control of motor speed by adjusting the frequency of the power supplied. Electrification policies often promote VFDs as a way to reduce energy waste in applications where motor speed varies according to demand. For example, pumps, fans, and conveyor systems benefit from variable frequency motors by consuming less power when full speed is unnecessary. As a result, variable frequency motor demand has grown in sectors like HVAC, water treatment, and material handling, where energy-efficient operation aligns with policy goals.
Fixed magnet motors are another type of motor seeing increased demand under electrification initiatives. These motors use permanent magnets in the rotor instead of traditional electromagnets, which reduces energy loss and improves efficiency. Fixed magnet motors are particularly common in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems due to their compact size and efficient performance. As governments promote the adoption of electric vehicles and invest in renewable energy projects, fixed magnet motors have become essential in meeting these new requirements. The reduction of greenhouse gas emissions in transportation and energy sectors means that fixed magnet motors will likely continue to see steady demand growth.
While electrification policies have driven positive change, the transition also presents challenges for motor manufacturers. For example, the increased demand for high-efficiency motors requires continuous improvements in motor design and manufacturing processes. Companies need to ensure that their three phase AC servo motors meet evolving standards for energy efficiency and durability. Similarly, producing variable frequency motors that operate reliably across a range of speeds requires advances in both motor and drive technology. Manufacturers must also address supply chain constraints for precious earth materials used in fixed magnet motors, as these materials are critical for magnet performance but subject to geopolitical and market fluctuations.
Another impact of electrification policies is the increased focus on standardization and regulation. Motors must comply with stricter energy efficiency standards set by governments and international bodies. These regulations encourage the use of motors that consume less electricity without sacrificing performance. For three phase AC servo motors, this means developing models with improved insulation, better cooling systems, and enhanced electronic control. Variable frequency motors must be paired with drives that meet harmonic distortion and electromagnetic compatibility requirements. Fixed magnet motors also face new testing protocols to ensure long-term reliability, especially in demanding applications like electric vehicles.
Electrification policies also influence the demand for custom and application-specific motor solutions. Many industries require motors tailored to their unique operational needs to maximize energy savings and meet environmental standards. The adaptability of three phase AC servo motors allows for precise control in specialized automation tasks, from robotics to packaging machinery. Variable frequency motors can be configured for a range of power ratings and speeds, providing flexibility in industries such as agriculture and manufacturing. Fixed magnet motors, with their compact and efficient design, can be integrated into various electric mobility platforms beyond cars, including e-bikes and drones, expanding their market reach.
As the electrification trend grows, so does the importance of research and development in motor technology. Advances in materials science, such as improved magnetic alloys and insulating materials, contribute to motor efficiency and longevity. Developments in electronics also enable better integration of three phase AC servo motors with control systems, while innovations in drive technology enhance the performance of variable frequency motors. For fixed magnet motors, ongoing work to reduce dependence on rare earth elements aims to make these motors more sustainable and cost-effective.
In summary, electrification policies worldwide are shaping the demand for electric motors in multiple ways. The need for energy efficiency, emissions reduction, and cleaner industrial practices has encouraged broader adoption of three phase AC servo motors, variable frequency motors, and fixed magnet motors. While this presents opportunities for growth, it also challenges manufacturers to innovate and adapt to new standards and market demands. As industries continue to embrace electrification, the motor sector will remain a key area of development, supporting the transition toward a more sustainable energy future.
-
Feedback


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى






