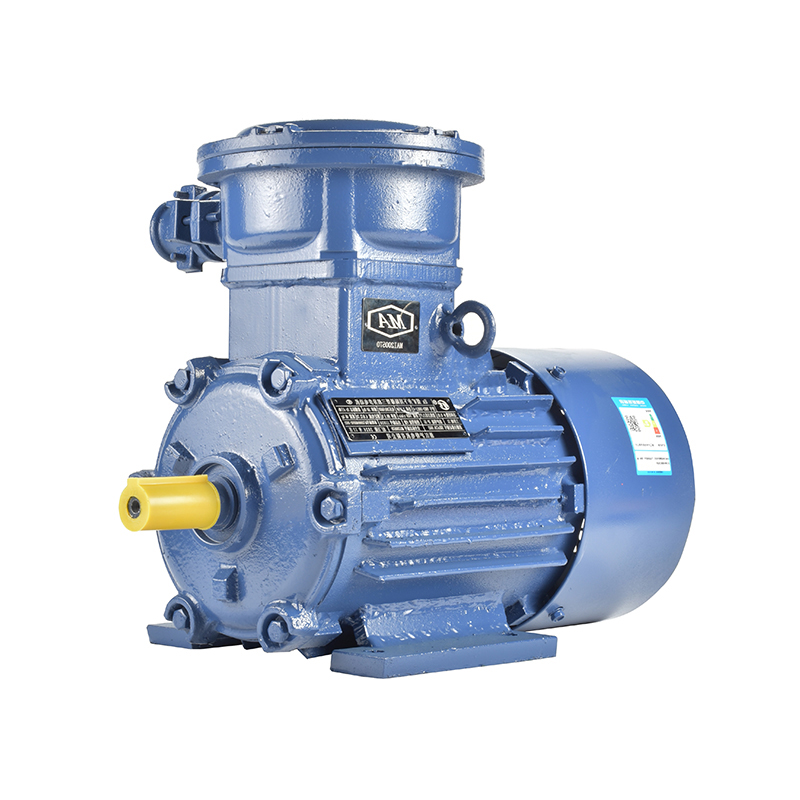
Emerging Trends In Three-Phase Asynchronous Motor Applications
In recent years, three-phase asynchronous motors have become more widely adopted across various industries due to their efficiency, durability, and broad adaptability. As modern production demands shift toward automation, energy management, and precise control, these motors have gradually moved into new application areas, influencing the design and integration of related motor systems.
A major development involves the expansion of three-phase asynchronous motors into systems that traditionally relied on simpler setups, such as the 1 phase asynchronous motor. While the 1 phase asynchronous motor is still used in smaller applications such as residential pumps or compressors, the shift toward more stable power delivery in industrial environments is encouraging more users to adopt the three-phase version. This trend has not only affected motor installations in manufacturing lines but also in sectors like agriculture and construction machinery.
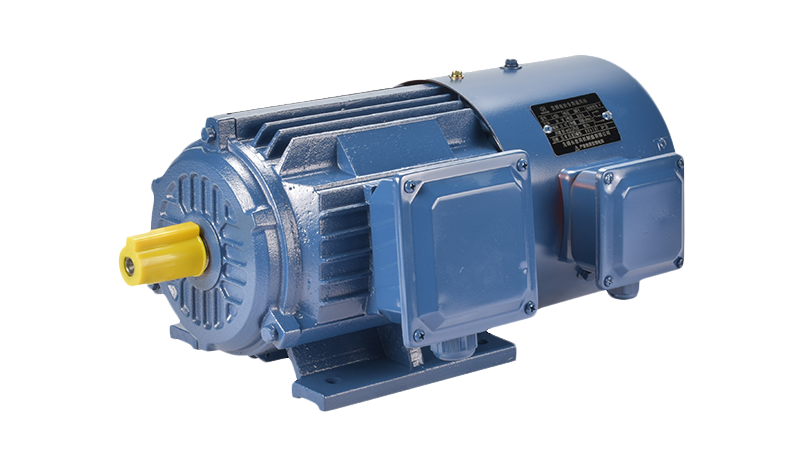

Interestingly, there is now growing interest in hybrid applications where both single phase three phase motor options are considered depending on location and load requirements. In rural or semi-urban locations where access to stable three-phase power might be limited, single phase three phase motor configurations are used to give flexibility to systems that need to run on different power supplies. Manufacturers are responding by designing motors that can easily switch or adapt to both modes depending on user preferences or regional power grid availability.
Another trend gaining momentum is the increased focus on motor speed and precision. While asynchronous motors are known for robustness, newer versions are being designed to interact more closely with digital control systems. These advancements have brought them into competition with the high speed synchronous motor in applications that require higher RPM stability and quick response times. For example, certain conveyor systems or textile machinery that once solely depended on the high speed synchronous motor are now considering asynchronous alternatives that come with advanced inverters and motor controllers, making them capable of delivering consistent performance under dynamic load conditions.
Still, the high speed synchronous motor remains the preferred option for equipment where phase synchronization is critical. However, three-phase asynchronous motors are narrowing the gap through improved rotor designs and better heat dissipation features. The result is a broader spectrum of use for these motors in areas like refrigeration systems, packaging equipment, and small-scale CNC machinery. In contrast, the 1 phase asynchronous motor remains mostly in light-duty equipment where compact size and low cost are more critical than torque or start-up performance.
In multi-motor systems, the growing use of smart drives and motor management units also enables single phase three phase motor setups to coexist more effectively. For instance, an automated production line may use a three-phase motor for the main conveyor, while auxiliary devices such as blowers or feeders use 1 phase asynchronous motor units to save space and wiring complexity. These mixed-use systems benefit from enhanced modularity and are easier to scale or modify depending on production needs.
The interaction between three-phase asynchronous motors and digital automation platforms is also shaping their future. Smart monitoring of motor temperature, load conditions, and efficiency metrics is becoming standard, reducing downtime and enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities. This development is also nudging some designers to replace high speed synchronous motor units in less demanding tasks, reallocating them to high-precision zones and letting asynchronous variants handle the rest.
Furthermore, the integration of wireless modules and programmable logic controllers into single phase three phase motor designs is allowing users in remote or mobile settings to better control motor behavior. This is particularly useful in agriculture, where equipment may need to operate far from centralized control rooms, and the 1 phase asynchronous motor often plays a supporting role in irrigation systems or grain processing units.
To conclude, three-phase asynchronous motors are evolving from traditional workhorses to versatile components capable of serving a broader range of applications. Their increasing overlap with 1 phase asynchronous motor, single phase three phase motor, and high speed synchronous motor technologies reflects a more interconnected and flexible motor ecosystem. As new demands emerge, especially in automation and energy-conscious operations, the roles of these motors are likely to continue blending, reshaping how industries approach motor selection and system design.
-
Feedback


 English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى






